Criteria for Diagnosis
The American Academy of Dermatology Diagnostic Criteria for AD include essential features (must be present for diagnosis)1:
- Pruritus
- Eczema (acute, subacute, chronic)
- Chronic or relapsing history
- Typical morphology and age-specific patterns including:
- Facial, neck, and extensor involvement in infants and children
- Current or previous flexural lesions in any age group
- Sparing of the groin and axillary regions
- Important features seen in most cases, adding support to the diagnosis:
- Early age of onset
- Atopy
- Personal and/or family history
- IgE reactivity
- Xerosis
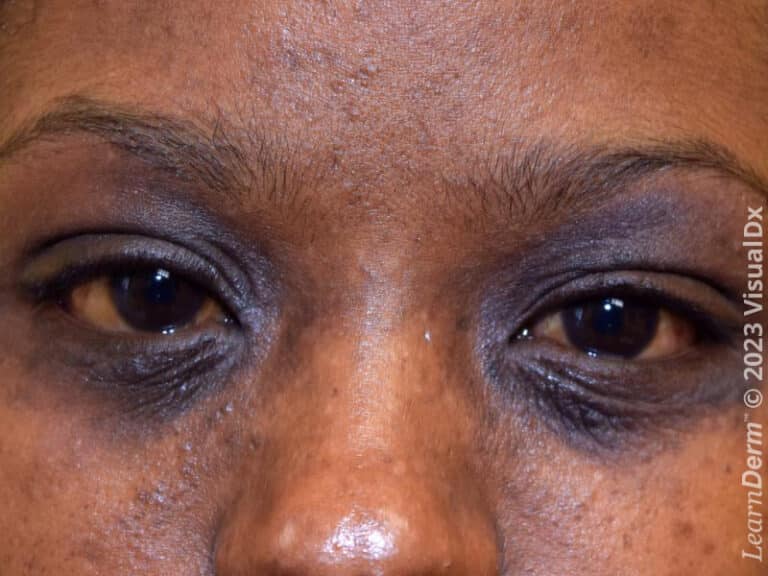
- Associated features – These clinical associations help to suggest the diagnosis of AD but are too nonspecific to be used for defining or detecting AD for research and epidemiologic studies:
- Atypical vascular responses (eg, facial pallor, white dermographism, delayed blanch response)
- Keratosis pilaris / pityriasis alba / hyperlinear palms / ichthyosis
- Ocular / periorbital changes
- Other regional findings (eg, perioral changes / periauricular lesions)
- Perifollicular accentuation / lichenification / prurigo lesions
1Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Chamlin SL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 1. Diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(2):338-351. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.10.010